Types of Point Machines Railway
* Nomenclature
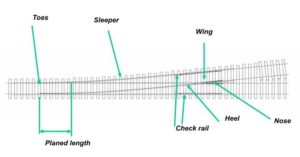
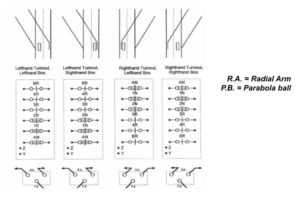
Right-hand turnout
* Common components
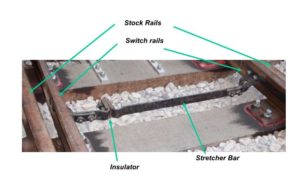
Stretcher Bars
* Legal requirement on turnouts
* Insulator required for correct track circuit operation
Point locking
* LUL provides facing point locks on all points where there are signalledmoves in a facing direction on or potential foul of passenger lines. This requirement includes shunting trains as well as passenger trains. Facing point locks may also be provided in depots or yards but are only mandatory when associated with a signalled passenger train moves.
Switch blade closed. If switch was open, the dab would be in the other port
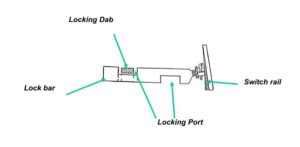
* In four foot / six foot Point locking is generally achieved using lock dogs on lock notches on the lock bars (Clamplocks use a different system, covered later)
* Lock dogs are moved out of the notches before the drive moves the switch rails and hence lock bars
Glass Enclosed valve for Point ground Lock
GLASS ENCLOSED(GE) VALVE TERMINALS
GLASS ENCLOSED(GE) FOR POINT GROUNDLOCK(2)
* This valve is a self contained unit with an integral transformer and rectifier, a soft iron core and, in some cases, a capacitor.
* The operation of the valve is controlled from a 100V or 110V AC supply. This is rectified to DC inside the valve enclosure to energise the coil so that the pin valve forced opened. Air is then supplied to the ground lock (WL) unit to lift the locking dab and free the points.
* Loss of air supply or power to the valve will cause the points to remain locked (fail safe arrangement).
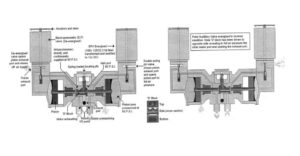
Point Auxiliary valve for Pneumatic Point Machines
POINT AUXILIARY NW/RW VALVE FOR PNEUMATIC POINT MACHINES
* The point auxiliary unit has two glass enclosed valve sattached to it: one used to control the supply of compressed air to drive the points normal and a second to drive the points reverse.
* The electrical feed to the corresponding point control is normally maintained at all times, even when all movement is completed. The exception to this is with clamp lock points where the valves are normally de-energised.
TYPES OF POINT MACHINES
* 4 Foot Point
* 6 Foot Point
* Chairlock Point
* Clamplock Point
* M63 or Style 63 Point (Same machine, different name)
* Surelock Point
FOUR FOOT POINTS
* The Four Foot point mechanisms are mechanical devices mounted within the four foot, normally mounted on the
continuous rail side.
* The versions of the 4ft point mechanism are categorized as left-hand and right-hand, depending on whether they are installed to the left or right side of the track center line, with points viewed in the facing direction.
* The following two assemblies differ between the left-hand and right-hand version of the 4ft point mechanism:
1. Point and lock mechanism
2. PL&D Box
FOUR FOOT ESCAPMENT
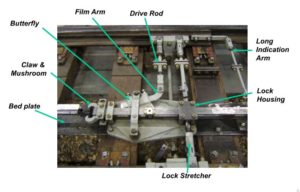
Escapement is part of mechanism of four foot points driven by motor and having locking dabs for facing point locks and locking ports for ground lock. The points are operated via a crank driven from the escapement.
FOUR FOOT POINTS
* Electro-pneumatic or Electro-hydraulic operation.
a. Electro-hydraulic operation on Central Line.
b. Electro-pneumatic operation on Jubilee, Northern and Piccadilly lines.
* Mounted between the running rails.
* Can be used on Bullhead and Flat Bottom rail.
* Right-handed or left-handed machines in operation.
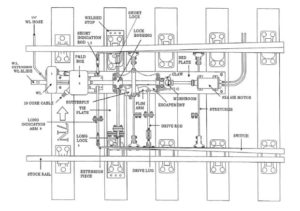
FOUR FOOT PL&D BOX
FOUR FOOT POINT MECHANISM
FOUR FOOT PL&D CONTACT ARRANGEMENT
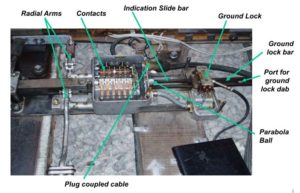
FOUR FOOT GROUND LOCK
* In addition to the facing point locks a ground lock must also be fitted to air operated points used for facing passenger train moves. The reason for this is certain types of machine maintain stored energy, which is capable of moving the points under fault conditions, and also without the ground lock the mechanism has very little resistance to movement under vibration.
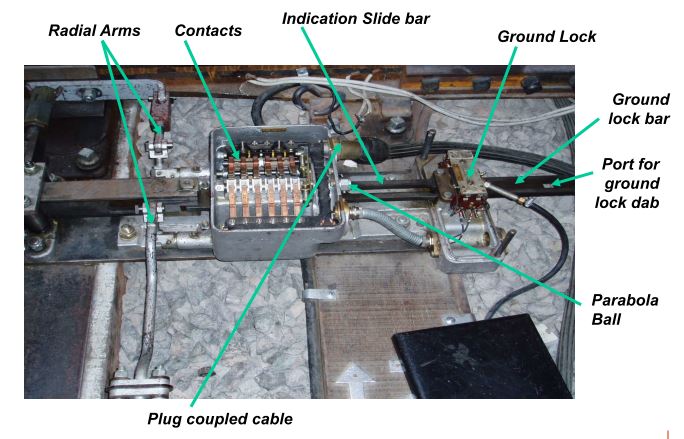
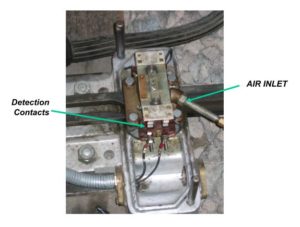
* A ground lock (WL) is a device which locks the points in position by inserting a dab into one of a pair of ports in the drive mechanism when the lifting magnet is de-energised and the points are fully in the correct position.
* The ground lock must be independently energised. A contact is made when the dab is fully in a locking port. It must also be detected; this can be done separately if not integral to the points detection as is the case with chair locks.
* It is not mandatory to provide either a facing point lock or ground lock when the points are only ever used for trailing moves, unless sectional route releasing is required in which case the points would be held by a ground lock.
FOUR FOOT GROUND LOCK






Hiya,
I’ve just been wondering. What does HW stand for?