Railway Electrification Advantages vs Disadvantages, Power supply
Advantages
1. Increased track capacity – Locomotive – Faster and more powerful
2. Less fuel consumption – with employment of regenerative braking fuel consumption is further lowered
3. Electric locomotives are cheaper, have long life, are less complex, have greater reliability, compared to Diesel counterpart
4. Environment friendly
Disadvantages
1. High basic capital cost
2. Possibility of electrical hazards
3. Visual intrusion of the overhead system
4. Electrical interference with communication systems
A C Electrification
A C Electrification traction supply system forms part of railway infrastructure owned and operated by Network Rail
System consists of Feeder stations, track sectioning cabins/locations, 25 KV overhead line contact system and associated SCADA systems
Power supply
Traction Power supplies are obtained generally from 132 KV National Grid system.
Supplies are taken by railway in duplicate as single phase current at 25 KV through 132/25 KV transformers, of 5 MVA to 26.5 MVA nominal capacity.
Supplies are taken to railway feeder stations.
Nominal supply voltage – 25 KV – single phase – 50 Hz.
Normal voltage range – Varies between 27.5 KV to 16.5 KV.
Normal frequency +/- 1%.
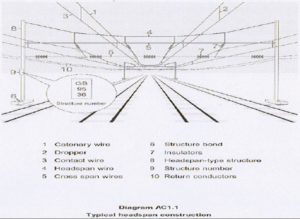
Electrification fixed equipment
Electrification fixed equipment – All the line side equipment that is provided for supplying electricity to electric trains
Includes the following:
Overhead line equipment (OLE) and its structures and foundations
Track side switching stations
Booster transformers
Bonding arrangements