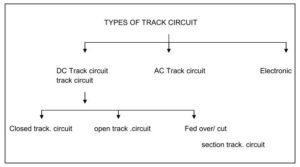
Railway Signalling Track Circuits | Closed TC | Open Track Circuit| Fed over track circuit
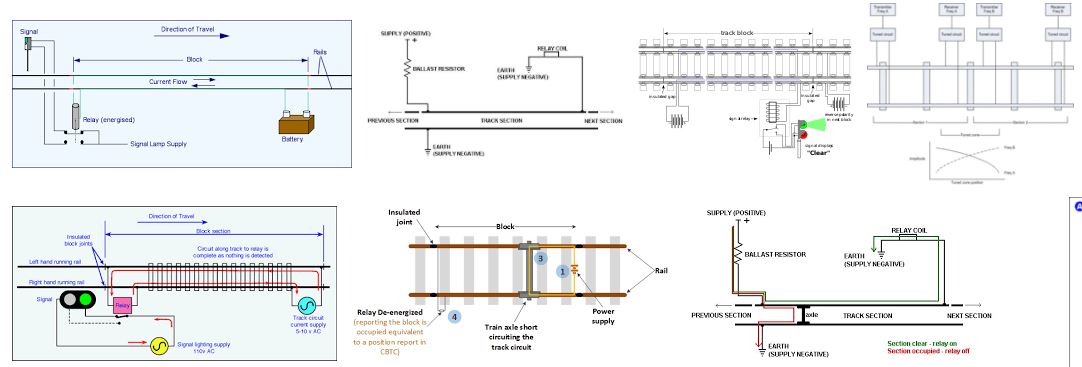
A track circuit is a vehicle detection device in which the running rails form part of an electrical circuit. The boundaries of track circuit are marked by insulation joints on the rail and rails are bonded at rail joints for better conductivity.
Uses of Track Circuits:
* For detecting the presence of vehicles or absence of vehicles within the limits of the track circuits.
* For locking the point when the train is on the point.
* Trolley protection circuit for axle counter to ensure wheels of easily removable trolleys are not counted.
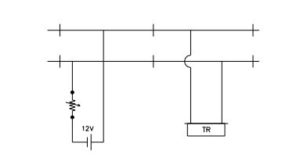
Closed TC: In this type current is always flowing through the relay. When train comes over the track, the supply to the relay is shunted and the relay de-energizes.
The smallest closed track circuit provided is of 26 meter length. The longest workable track circuit depends on the Ballast Resistance (i.e., Resistance across rails offered by the stone chips placed below the rail to support track), This ballast decides the leakage current. In other words ballast resistance appears across or in parallel with relay coil
resistance.
Open Track Circuit:
Open track circuit is one in which the track relay is normally de-energized and picks up only when train comes on the track.
In this track circuit, any disconnection with train on the track will drop the relay and failure on unsafe side will take place, as the relay will show track is clear under occupation. Hence this track circuit can be used for short length only i.e., 26 Mts. Now a days open track circuits are not used.
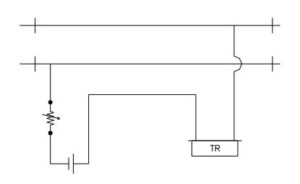
Fed over track circuit:
It is a sub division of track circuit. This is generally adopted when it is not possible to work a long track due to inability to maintain prescribed parameters like ballast resistance for fail safe working of track circuit. Instead of dividing it in to independent track circuits, the first track circuit is fed by the usual battery and relay arrangement.
The feed to the second track is taken through the front contact of the track relay which controls the first track and so on. The last track relay can serve to indicate occupancy or clearance of the portions of all track circuits.