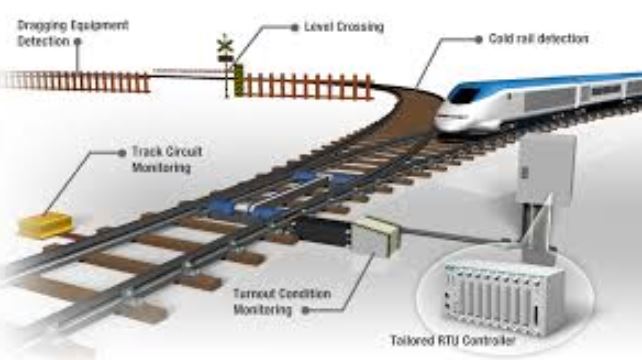
Definition of Railway Signalling Equipment
Rails- Is an iron track, it is the base of the Railway transport. The train moves on the track
Sleepers – Which is used to place the rails, and it gives support to the tracks.
Wooden- in olden day, the wooden track was used, but now a day wood is rare, so we use steel rails
Steel – the steel rail also having some problem, if we use steel rail, we can not isolate the tracks.
Concrete – so we move to concrete rails. It gives good support to the tracks, and we can isolate the tracks anywhere.
Ballast – It is a crushed stones, which makes a trackbed. The track lay on the ballast (Track bed). It holds the track in place.
Web of rail – It is the part of rail. which is placed between the rail feet and head.
Running edge – it is the inner side of the track. The flange moves in this side.
Flange- It the projection of the train wheel. Which is used to keep the train inside the Track.
Axle – it is the part of train, the two wheels of each bogies connected through the axle.
Turnout – It is normally known as Divergence. It can place either right side or left side.
Curve – Normally the bended track is called curves.
Crossover – Divergent from one track to another.
Points (Switches & Crossing) – Point is a section, which is used to turn the train in one Track to another.
Normal position- In the point is set for straight route, is called normal position.
Reverse position– if the point is set for divergent route, which is called reverse position. Signaling plan shows normal position of points
Diamond crossing – The name “Diamond Crossing” coming from its shape. To track cut Each other is called crossing.
Fixed diamond – In this crossing, we can not move the train in one track to another. The train can move only specified track.
Switch diamond – In this crossing, some switching arrangements are provided for the gap between the switch rail & stock rail. So the train can move higher speed in this crossing.
Nose of the crossing – In the crossing section, the two tracks connected together & made “V” shape. That is called Nose of the crossing.
Toe of the switch – For smooth moving, the width of the switch rail is reduced towards its End. That end is known as “toe”.
Heel – This is used for giving flexibility to the switch rail.
BS113A rail profile (old)– One type of rail, was used by British railway.
CEN60 rail profile-
IRJ – Insulated Rail Joint (or block joints)
Insulated Rail Joints:
(1) Dry joints
(2) Glued joints
NR60 geometry for switches and crossings
RT60 geometry (earlier geometry)
NR60C
NR60D
NR60E
Cant
Swing nose crossing
Gauge: Standard gauge 1.432m
Tilting trains
Permissible speed
Enhanced permissible speed
Cant deficiency
Transition curve
UIC60