Railway Track Circuits
What is a Track circuit?
OUTLINE
1. Introduction
2. Components
3. Working
4. Do’s & Don’t
5. Other technology
6. Present era of technology
7. Conclusion
INTRODUCTION
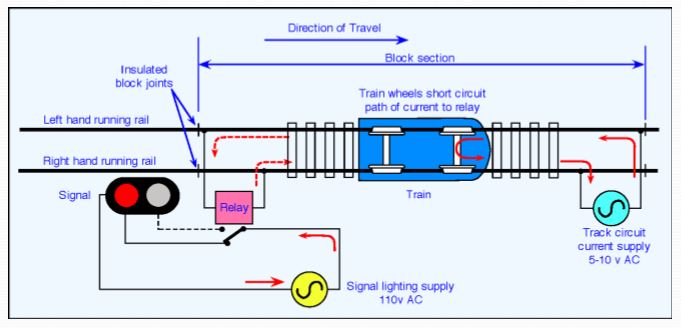
1. Track circuit is a simple electrical device used to detect the Presence/Absence of trains on the rails.
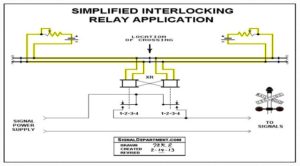
2. Track circuit is one of the primary inputs for a signal interlocking plant.
3. The signal cannot be green while there is another train on track segment ahead.
COMPONENTS
1. Battery.
2. Track Relay.
3. Adjustable resistance.
4. Insulated rail joints.
Battery
1. Gravity cells are used.
Relay
1. A relay is an electrically operated switch.
2. The Relay switch connections are usually labeled common, normally closed, normally open.
Adjustable Resistance
TRc – Track Lead Resistance at the feed end
TRr – Track lead Resistance at Relay end
RT – Regulating Resistance
Rr – Rail Resistance (Rail joint Resistance)
RB – Ballast Resistance
TSR – Train Shunt Resistance
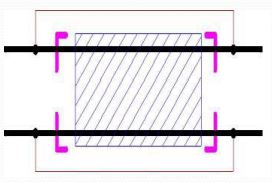
Insulated rail joints
1. Track circuit required insulated rail joint for isolating it the adjacent track circuit.
2. Nylon IRJ
3. Glued IRJ
Track circuit bonding
Rail bonds need to be provided on track circuits have to point turnout them.
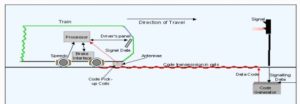
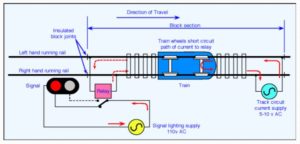
WORKING
1. The portion of the Track which is to be Track circuited, is first provided with wooden or RCC sleepers and then the rails are insulated from the rest of the Track by the provision of Insulated rail joints.
2. At one end of the Track circuit feed is connected and at the other end, the track relay is connected.
3. When the track portion is not occupied by trains, the fed is available for track relay and the relay is in energized condition.
When a train occupies the track circuit portion, the axel & wheels shunt the track much of the circuit current is passed through the wheels due to less resistive path and very less current is available for track relay, which is not sufficient enough to pick up the relay.
DEAD SECTION
1. Those sections of the track circuit in which occupation by a vehicle cannot be detected.
2. Curved track.
3. Cross.
4. Bridge.
DO’S & DON’T
1. Top up distilled water if the electrolyte level is low in batteries.
2. Change the relay which is due to for overhauling.
3. Replace the damaged and corroded bonding wires.
4. Do not Tilt the relay.
5. Do not Test the track circuit by shunting with a wire only.
6. Track circuit does not get shunted properly by vehicles.
7. Its working length is dependent on the immunity of the track relay.
OTHER TECHNOLOGY
1. AC Track circuit.
2. Audio Frequency Track circuit.
3. Axle Counter.
PRESENT ERA
1. Indian Railways is installing state-of-art technology along train tracks to detect of faults and defective parts in coaches, wagons, and locomotives.
2. The new system, which uses high-speed infrared and digital cameras, will replace a physical examination of the wagons by railway staff.
3. The project, which will be run as a trial project will be installed at 10 locations at an estimated cost of 73 crore rupees in the first phase.
CONCLUSION
1. DC Track circuits are the simplest, least costly, and most reliable type of track circuit.
2. Nowadays for signaling purposes, trains are monitored automatically by means of TRACK CIRCUIT.
3. Track circuits play important role in stop accidents, traffic.
Railways Track Circuits Wikipedia Link