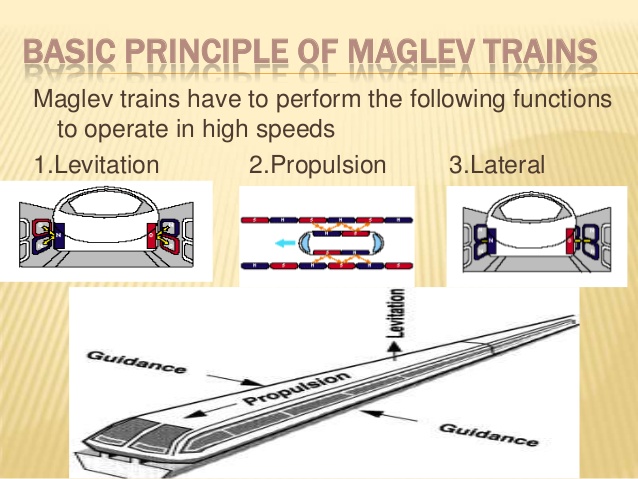
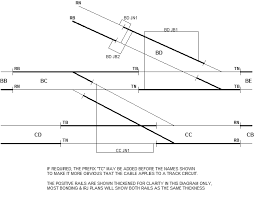
Basic Track Structure Point & Crossing
Basic Track Structure Point & Crossing Basic Track Structure Point & Crossing:- Trains run on a dedicated line. A line consists of two rails running parallel to each other. This is also called „Track „. The width of the track is 5‟6”in Broad gauge (B.G) The track is represented in Signalling plans by a single […]
Continue Reading