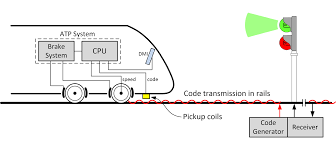
Railway Signalling Coded Track Circuits D.C. Coded Track Circuits
Railway Signalling Coded Track Circuits D.C. Coded Track Circuits Coded Track Circuits • D.C. Relay Coded Track Circuits • Solid-State Coded Track Circuits – Electrocode – Microtrax D.C. Coded Track Circuits 1. Transmitter – Sends a coded D.C. voltage (Square Wave) 2. Receiver – Decodes signal 3. Dependent on the code rate, receiver will : […]
Continue Reading