Metro Rail Advanced Signalling System
Metro Rail in India
Kolkata Metro: The Kolkata Metro is a mass rapid transit system serving the city of Kolkata. It was the first such form of transportation in India, opening commercial services in 1984. Delhi Metro: Planning for the metro started in 1984 when the DDA and the Urban Arts Commission came up with a proposal for developing a multi-modal transport system for the city. The Government of India and Delhi jointly set up the Delhi Metro Rail Corporation (DMRC) in 1995. Construction started in 1998, and the first section opened in 2002. Rolling stock 179 trains, the total length of track 189.63 kilometers with 142 stations of which 35 are underground.
Bangalore Metro: Opened in 2010. And Construction started for Mumbai, Hyderabad & Chennai Metro.
Signalling
1. For ensuring Safe train movement.
2. Signalling is used for increased line capacity.
3. Signaling is mean of communication to Impart Non Verbal information to Train Operator.
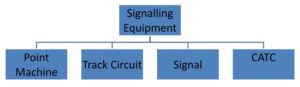
Signalling Equipment
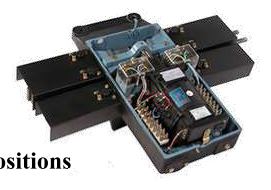
POINT MACHINE
The point means a connection used to connect one line to another for the purpose of making a movement from one line to another line.
1. POINT MACHINE IN DEPOT
2. POINT MACHINE IN MAINLINE
Point Machine: – is a signaling gear that is used for diverting train/ vehicle from one line to another.
Point Position: – Point has two positions
1. NORMAL
2. REVERSE
ELECTRIC KEY TRANSMITTER
(a) NORMAL: – means that Position of a point which is normally set for most of the trains.
(b) REVERSE: – means that the Position of a point is not normally set for most of the trains but when operated by point machine can cause train/ vehicle to change to another line.
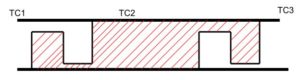
Track Circuit
1. Track circuit is a device that is used for detecting the presence or absence of a train.
2. Apart from detection of train presence, it is used for SACEM (Systeme d’Aide à la Conduite à l’Exploitation et à la Maintenance ) data transmission.
Target point sent to the train to train, OCC, DCC, SCR, SER, etc.
SMARTWAY DIGITAL TRACK CIRCUITS (SDTC) SDTC cubicle, and TWC rack RELAYS/Relay panel
All signal elements like mainline signals, depot signals, point machines, shunt signals other than Track Circuits need to be proved by relays. The inputs from the field first come to the relay panel.
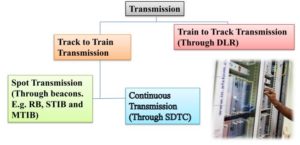
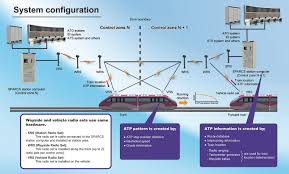
Trackside ATC Equipment
Trackside ATC equipment communicates with the train-born ATC for the safe running of the train. ATC cubicle is called 2 out of 3 cubicles (2oo3). It is SIL(Target point sent ) to the train B 4 system. Communication is two-way. The Transmission between Trackside and Train can be classified as
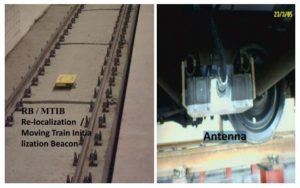
STIB (DL/DLR- Down Link Receptor) Stationary Train Initialization Beacon
Impedance Bonds
A connection box, usually mounted between the rails, which provides continuity with the return signal/current.
Signal
Cab Signal
1. Cab signal is an indication provided inside the Train Operator’s cab in terms of speed code.
2. Proceed: Speed Code other than zero
3. Stop: Speed code is zero
1. MMI: Man-Machine Interface Odometer speed sensor
2. DMI: Direct Media Interface
Fixed Signal
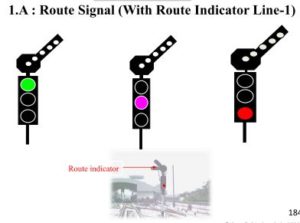
1.A: Route Signal (With Route Indicator Line-1)
Route Signal
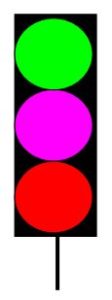
Green : Proceed: Route set, locked and the track circuits to the next route signal are clears. (or the two blocks are clear).
Violet: Conditional proceed: Route set and locked, and the first track circuit after the signal is clear. (or two-track circuits of the cross over). or the green aspect is failed or Route Indicator (or repeater Route indicator is not lit if control given for it).
Red : Stop: Route not set and locked, or the first track circuit after the signal is occupied (or one of the two-track circuits for a cross over).
Shunt Signal
1. The Shunt signal has three lamps to display different indications.
2. There are two types of indications.
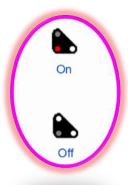
3. Two lunar white horizontal lamps: Stop (Normal, ON, restrictive aspect) Route not set and locked, or if the route includes track circuits one of them is occupied.
4. Two lunar white lamps at 45°in the left-hand upper quadrant: proceed (or Clear, OFF, permissive aspect), Route set and locked, and if the route includes track circuits all of them are clear.
Repeater Signal
Buffer Stop Signal
Used at
1. the ends of the line ;
2. the ends of the siding in the line and in the depot ;
3. the ends of the test track in the depot ;
4. These signal permanently show a red aspect
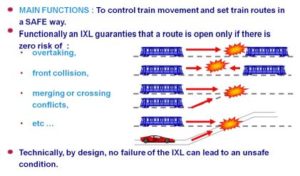
Interlocking means the arrangement of signals, points, and other appliances operated from lever frame or panel electrically, mechanically or both in such a way that their operation must perform in the proper sequence to ensure safety. In CBI (Computer Based Interlocking) Monitor and Control Signaling Equipment Track Circuits, Points, Signals, Cycles and Routes
System of working
CATC (Continuous Automatic Train Control)
• CATC’s Subsystem :
– ATS (Automatic Train Supervision)
– ATC (Automatic Train Control)
– ATP (Automatic Train Protection )
– ATO (Automatic Train Operation )
Related Speed. Continuous monitoring of braking. Audiovisual warning and application of brakes, if necessary. Maintaining safety distance between trains. Monitoring of stopping point. Releasing doors on the correct side of the platform when the train comes to a stop.
Signal Set SAFE Way
Rail Transport in India – 1849, in 1951 Nationalized, in 1853 introduced. 135,000 km Track, 60,000 Rolling stock, 20 million passengers per day.
Meter gauge 1,000 mm.
Narrow gauge 1,067 mm.
Broad-gauge 1435 mm.
Track gauge 1676 mm.
Metro signaling system PDF Link
Metro rolling stock India Link
FAQs
1. What is Metro rolling stock?
Ans. The rolling stock is based on lightweight stainless steel, Aluminum‐ bodied three‐car formations, having a trailer car between two motored driving cars.