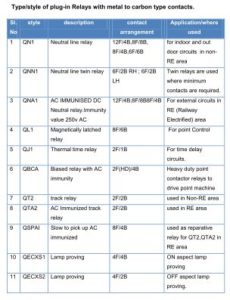
Railways Signalling Relays | Shelf type Relays
Relays
Relay is an electromagnetic device which is used to convey messages electrically from one circuit to another circuit through a set of contacts (back or front contacts)and works on the principle of electromagnetism.
Relays are classified as :
According to the source of power applied – DC Relays & AC Relays.
According to mounting – Shelf type & plug-in type.
According to the application. – Line relays & track relays.
According to polarity on coils – Neutral relays, polarized relays and Biased relays
According to contact material – Metal to carbon contact relays (non proved)
– Metal to Metal contact relays (proved)
According to importance of circuit – Vital relay & non vital relays.
According to immunization – AC immunized DC relays,
Non AC immunized D.C .Relays
Shelf type Relays
* These relays are classified as neutral line and track relays. Both can be of AC Immunized or non AC immunized.
* Contact elements of front contact are carbon and metal for both back & movable contacts.
* Contact resistance for front contact is 0.2 ohms and back contacts are 0.5 ohms.
* Continuous contact current capacity is 3 Amps.
| Function | line relay | Track relay |
| Working voltage | Normal 12 V DC | Minimum 125% & Maximum 250% of rated pickup voltage of relay. |
| Coil resistance | Two coils of each 4.5ohm Parallel connected 2.25ohm. series connected 9.0ohm. |
Two coil 500 ohm each |
| Standard contact Arrangement | 4F/B & 6F/B (All are dependent) | 2F/B ;2F-2F/B |
| Usage | other than tracks | connected to track only |
| Sensitivity | LOW | HIGH |
| Periodic Overhaul | 15 years | 10 years |
| Working | More voltage | less voltage |
| Minimum% release | 50% class ”B” | 68% |
| (Drop away /Pickup) | 60% class “A” | |
| Principle of working | Without any current De-energiser |
Reduction in current causes relay to drop. |
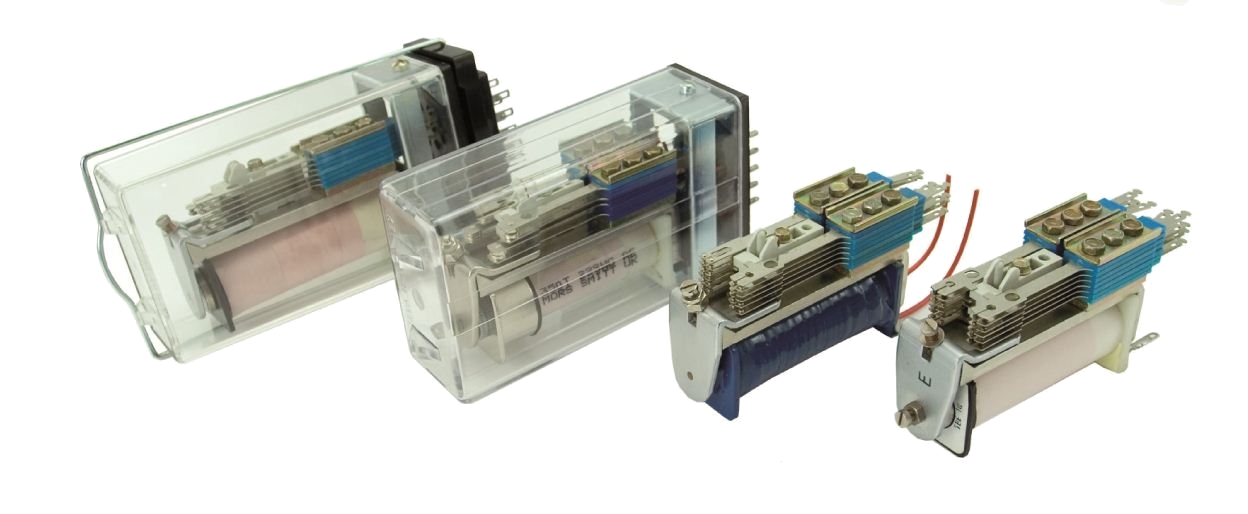
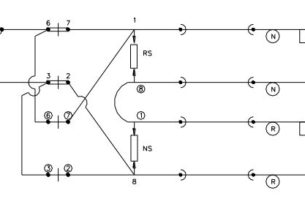
Plug- in type relays
Basic Constructional Features:
* Common plug board for all relays.
* Plug & socket kind of interconnection between plug board and relay.
* Retaining clip to hold the relay firmly.
* Connectors positively locked in the plugboard can be withdrawn by a special tool.
* Terminating wires on the connectors is both by crimping and soldering.
* Registration device with specified code combination to prevent interchanging of relays.
* Relay filled with gasket for moisture protection.
* Maximum numbers of contact are 16 independent metal to carbon type.
* Continuous current carrying of contact: 3 amps.
* Switching capacity : 2 Amps.
Metal to metal contact plug-in type relays
These relays fall under the category of proved type relays. Since metal to metal contact can cause fusion or welding when current is interrupted due to circuit making or breaking, proving of back contact is necessary. Otherwise cutting the power to the relay can not be assumed to drop and break the front contacts (picked up contact due to
exercitation of the relay)
Specification:
Coil resistance — 1260 to 1840 ohms
Rated voltage — 60V DC
Minimum number of contacts — 8 Nos.
Contacts combination — 4F/ 4B; 5F/3B; and 6F/2B.
Contact rating. — 5 Amps
Relays supplied can be of neutral relays, interlocked relays or lamp proving relays. Further these relays may be supplied as Mini group consists of two relays on a base plate pre-wired. Minor group with of 15 relays for route, signal functions. Major group with of 30 relays for point functions.


Hello
Railway signaling will be used.
We need the following products
Annual consumption 100 pcs.
————————————————————
CODE TYPE VOLTAGE CONTACT OHMS
——- ——- ———— ———— ———–
QN1 24 V DC 8F8B 350 = 6 Pieces
QT2 0,5 V DC 2F1B 4 = 6 Pieces
6 + 6 = 12 Set (Relay,Socket and contacts )
I would like your address delivery price.
Shipping address:
Fevzi Çakmak Mh.Özlem Cad. No : 22/E Posta kod.42050 Karatay / Konya – TÜRKİYE Gsm :+90 551 023 56 56 e-mail = [email protected]
thank you Mehmet Döner
Bonjour chers messieurs,
Notre société de la République de Moldavie est intéressée à établir des contacts avec
fabricants de relais électromagnétiques pour l’automatisation et la télémécanique ferroviaire.
Je suis intéressé par les relais électromagnétiques neutres enfichables.
Veuillez nous indiquer si votre entreprise produit de tels biens, leurs prix, leurs conditions.
Merci beaucoup ,
Cordialement, Directeur SRL “ISAF-EXIM” Valeriu Mitsa