Metro Safety Concept & Practices in Signalling Dubai
Signalling and Safety Systems Metro Safety Concept & Practices in Signalling Dubai
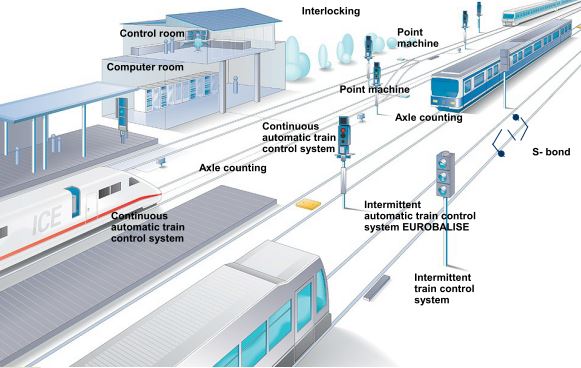
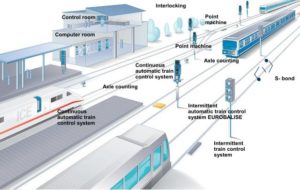
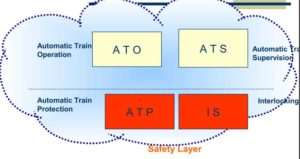
Signalling Overview
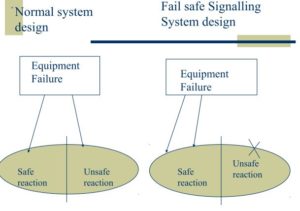
What is Fail Safety?
1. Failures- whether Equipment or Human
2. can be minimized
3. but can not be eliminated
4. Therefore, steps are required to be taken to ensure that there is no unsafe effect of failure
5. Signalling Systems are designed in such a way that every Failure has a safe Reaction
This is called Fail-Safe Principle
Fail-Safe Principle
1. Fundamental principle of design of Signalling system is:
2. safe state corresponds to the lowest energy level
3. to keep the system in a permissive state, constant energy/effort should be applied
4. This ensures that due to any inadvertent situation or failure, the system comes back to the state of lowest energy—ie. Safe Sate
Fail – safety
1. Fail-safe Principle is adopted in the design of all signalling systems- mechanical, relay-based as well as software-based systems
2. Example- Semaphore Signal
3. Mechanical design is such that the” stop” aspect is the stable state
4. Constant Force required to keep required to keep the signalling “ proceed” aspect.
5. Signal returns to the “stop” aspect in case of breakage of transmission wire or any other failure.
Fail – Safety-Examples
1. Signalling Relays:
2. Stable state- Dropped (Maintained by gravity/spring action)- safe state
3. Red signal aspect controlled by Relay-” dropped”- which is the lowest energy state.
4. permissive aspect controlled by Relay –” picked up”
5. Constant current required to maintain the relay in “picked Up”
Software-Based Systems
1. Software-based Signalling systems require repeated positive action to be taken by both, software as well as hardware to keep it in a permissive state.
2. Disruption of this positive action due to any failure results in the reversion of the system to a safe state.
Microprocessor and another component
Disadvantage Advantage
Are not fail-safe Speed
Don’t have well able to perform
complex task
defined failure modes
Are not reliable enough Miniature size
to meet 10 -9 unsafe
failures/our. They are Low price
approx. 10 -5 to 10 -6
Then How is Safety Achieved?
1. Employ more resources than required (redundancy)(both hardware & software)
2. Self-check procedures to detect a fault within a given time period dt such that prob. of occurrence of a fault within it is < 10 -9
3. watchdog timers
What is Redundancy?
1. Redundancy:
2. Is the use of additional resources(whether hardware or software) than required for the normal functioning of the system
3. The additional resources should be configured judiciously to obtain max. the advantage in terms of safety and reliability
4. The amount and type of additional resources and their configuration will depend on the safety and reliability requirements.
Types of redundancy
1. Dual hardware redundancy
2. Dual hardware redundancy with 100% standby
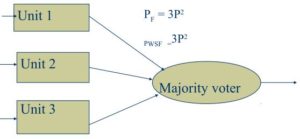
3. Triple modular redundancy(TMR)
4. Software redundancy-single hardware
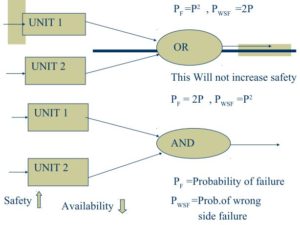
Dual hardware Redundancy (2 oo2)
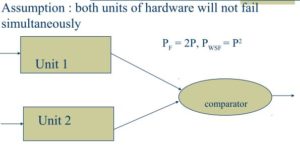
Dual HW red+100% standby (2-2oo2)
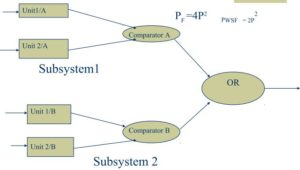
Triple Modular Red. (TMR) (2oo3)
Asmpn: 2 units will not fail simultaneously
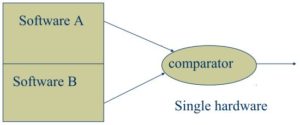
Metro Safety Concept & Practices in Signalling Dubai Software redundancy- single hardware
Assman: independent Softwares will react differently for an HW fault
Self Check & Watchdog timers
1. Periodical check of microprocessor, buses, memory, peripheral especially input circuits
2. Watchdog timers within a specified time window if the command is not received then the system goes to a safe state.
Essentials of Interlocking (as per Indian railway SEM)
1. It shall not be possible to take ‘OFF’ a running signal unless all points including isolation are correctly set, all facing points are locked and all interlocked level crossing is closed and locked against public road for the line on which the train will travel including overlap.
2. After the signal has been taken ‘OFF’ it shall not be possible to move any points or lock on the route, including overlap and isolation, nor to release any interlocked gates until the signal is replaced the ‘ON’ position.
3. It shall not be possible to take ‘OFF’ at the same time, any two fixed signals which can lead to any conflicting movements.
4. Where feasible, points shall be so interlocked as to avoid any conflicting movement.
Dubai Metro Construction company
Dubai Metro train manufacturer