Metro Rail Telephone System Training
Metro Rail Telephone System Training : The purpose of Telephone system is to provide voice and data communication for DMRC. At each station, communication is provided through EPABX. All the telephone systems are connected together to form a telephone network over FOTS. There are two independent networks established between the stations – EPABX network and direct line network. One EPABX system is used to implement these two networks independently. Separate interfaces are used inside the PABX for telephone network and direct line network.
EPABX network is used for the administrative communication purposes, including communication with outside DMRC. This includes extensions for the staff concerned with administration, trunks to PSTN using DID and CO trunks, digital phones, and analog phones.
A direct line Network is used for operational communication purposes. The communication will be between the stations and OCC and depots. It includes analog extensions digital extensions used as direct line telephones at stations and direct line consoles and group call sets at OCC and depots. It also has leased lines to DVB, Fire, Police, and Ambulance for rapid communication.
EPABX: The EPABX stands for Electronic Private Automatic Branch Exchange. It is an exchange that serves a particular business or office, as opposed to one that a common carrier or telephone company operates for many businesses or for the general public. It is also known as PABX. This system works on -48 V DC from SMPS. Data is processed at a rate of 64k bps.
Functionally, the PBX performs four main call processing duties:
Establishing connections (circuits) between the telephone sets of two users (e.g. mapping a dialed number to a physical phone, ensuring the phone isn’t already busy)
1. Maintaining such connections as long as the users require them (i.e. channeling voice signals between the users)
2. Disconnecting those connections as per the user’s requirement
3. Providing information for accounting purposes (e.g. metering calls)
EPABX System at OCC: Telephone system shall interface to the radio system to enable radio users to initiate and receive calls to/ from EPABX extension or to MTNL or TATA INDICOM telephones.
Centralized Digital Recording System: The telephone system is equipped with a CDRS for recording of designed lines, emergency PAS announcements and designated conversion system.
Network Management System: The telephone network including EPABX and DLTC system is monitored, supervised and controlled by a NMS.
EPABX rack is divided in two shelves:
a. Shelf 0
b. Shelf 1
These shelves can be extended according to requirements
OMNI PCX -4400 is further sub-divided into two types. Which are given below:-
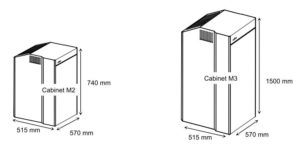
1-M 2 TYPE Exchange-Installed at each station of DMRC.
2- M 3 TYPE Exchange-Installed at OCC SHPK,OCC BRKR,KGRC,KPD ,SHPKD and all Depot of Phase-II project.
In DMRC two CPU are used for redundancy purpose. In M2 type exchange Main CPU is installed in Sl.No.6 and redundant CPU is installed in Sl.No.10.In case of any failure , redundant CPU becomes main. Main CPU is installed in sl.No.20 and redundant CPU is installed in Sl.No.6 in M3 type exchange.
Units
Cards In EPABX
UA boards (UA16, UA32) : 16 to 32 dedicated digital sets .The UA board allows sets and UA terminals to be connected.
Z boards (Z12, Z24): 12 to 24 analog terminals.This board allows 12 or 24 analog terminals to be connected to the ACT system.
PRA / PRA2 board : 1 T2 for EPABX interface. The PRA board allows connecting the system to the ISDN network and private network (2Mbits link; ABC-F protocol).
NDDI board : 8 analog interfaces
VG board : 2 INTEL flash cards ( 2×4 Mo) for voice guides.The VG (Voice Guides) board is a auxiliary-ACT board . It generate the voice guides (VG).
GPA board : 5 DSP which can be used for 29-way conference calls , recording voice guides and R2 frequency receivers. The GPA (General P urpose A uxiliary) board fulfils different speech processing functions. It can also process, in detection or generation, tones and multifrequencies used within the different public or private networks.
INTOF board : Interconnection of ACTs in Multi-ACT configuration for long distance : The INTOF board (INTerconnection on Optical Fiber) carries out a connection between a main ACT and a local or remote peripheral ACT.
MMSFD board : The Mass Memory Support (MMS) board is a physical support for the OmniPCX 4400 mass memory. It is 3.5″ diskette drive (MMSFD board). This board used for taking back up on floppy disk or restore data’s from floppy disk.
CPU board : The CPU processing unit is the heart of the PABX. It processes system applications (telephone applications, telematic applications, voicemail applications, etc.). It generates clock signals and tones for the entire ACT.
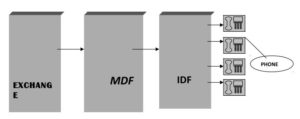
Connection of Phones at a Station
IDF-Intermediate Distribution Frame
MDF-Main Distribution Frame
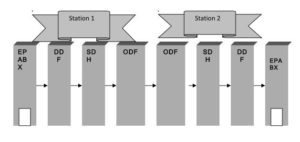
Stations Connectivity
DDF-Digital Distribution Frame
SDH-Synchronous Digital Hierarchy
ODF-Optical distribution Frame
Types of networks:
1-EPABX NETWORK: EPABX network is used for the administrative communication purposes, including communication with outside DMRC. This includes extensions for the staff concerned with administration, trunks to PSTN using DID and CO trunks, digital phones, and analog phones. The EPABX Switch Network will use the ALCATEL 4400 PABX system and also Alcatel Transmission Equipment between the stations, using 2 Mbps links to Fiber Optic Transmission System (FOTS).
2-DIRECT LINE NETWORK: Direct line Network is used for the operational communication purposes. The communication will be
between the stations and OCC and depots. It includes analog extensions used as direct line telephones at stations and direct line consoles and group call sets at OCC and depots. It also has leased lines to DVB, Fire, Police and Ambulance for rapid communication.
Types of Telephone instruments used in DMRC
1 Analog phone
2 Analog feature phone
3 Digital Phone
4 Direct line phone
5 Console
Types of phones used:
1. Digital: (work on 48-54V DC)
a) Digital phone
b) Direct line console
2. Analog: (work on 38-40V DC): Priority of digital phones is kept higher than that of analog phones, that is, digital phone can take channel from analog port if all digital ports are busy.
Numbering plan:
1. Analog:
Two digit station code + three digit specific room no.
Eg: For 89500 number,
2. Direct line:
1. 6 + two digit station code + two digit specific room no.
2. Eg: For 68950 number,
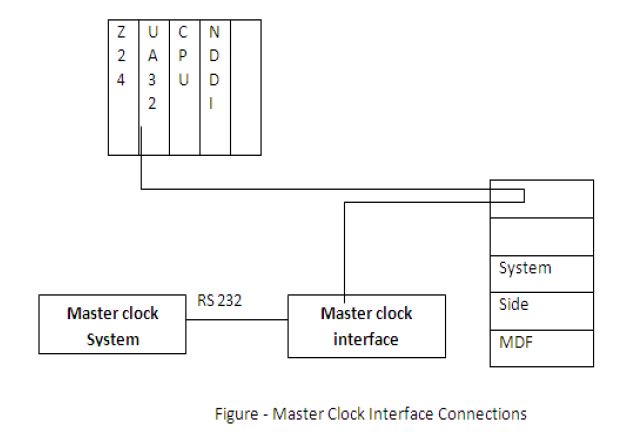
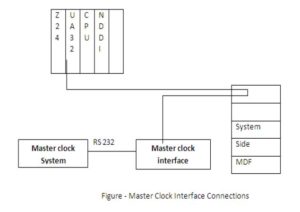
3.Interface with Master Clock System